Taco Bell Bean and Cheese Burrito: Taco Bell Bean And Cheese Burrito Nutrition
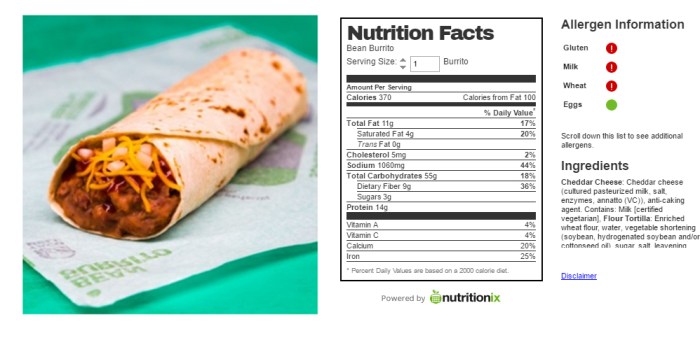
Taco bell bean and cheese burrito nutrition – The Taco Bell Bean and Cheese Burrito is a classic fast-food option, known for its simplicity and affordability. Understanding its ingredients and their nutritional contributions can help consumers make informed choices about their diet. This section provides a detailed breakdown of the burrito’s typical composition.
Ingredient Breakdown of the Taco Bell Bean and Cheese Burrito
The Taco Bell Bean and Cheese Burrito’s ingredients are relatively straightforward, primarily consisting of beans, cheese, and a flour tortilla. However, slight variations in ingredients and quantities may occur depending on location and preparation. The following table provides an estimated breakdown of the ingredients and their approximate weight or volume. It is important to note that these are estimates, and actual values may differ slightly.
| Ingredient | Weight/Volume (Approximate) | Nutritional Contribution |
|---|---|---|
| Flour Tortilla | 60-70 grams | Provides carbohydrates for energy; source of fiber. |
| Refried Beans | 60-70 grams | Source of protein and fiber; contributes to satiety. Contains carbohydrates and some micronutrients. |
| Cheddar Cheese | 20-30 grams | Provides protein and calcium; source of fat and saturated fat. |
Comparison with Similar Products
The Taco Bell Bean and Cheese Burrito’s nutritional profile provides a useful benchmark against which to compare similar offerings from competing fast-food chains. Analyzing these comparisons reveals important differences in caloric density, macronutrient ratios, and micronutrient content, influencing the overall nutritional value and suitability for various dietary needs. Understanding these distinctions allows consumers to make informed choices aligned with their health goals.Analyzing the macronutrient composition – specifically protein, carbohydrates, and fats – alongside the overall caloric content, offers valuable insight into the relative energy density and satiety potential of these fast-food options.
Similarly, examining micronutrient profiles, such as fiber content and sodium levels, provides a clearer picture of the potential health impacts of consuming these burritos regularly.
Nutritional Comparison of Bean and Cheese Burritos
The following table compares the Taco Bell Bean and Cheese Burrito with similar items from other fast-food chains. Note that nutritional information can vary slightly depending on location and preparation methods. Data presented here represents average values from publicly available nutritional information on respective company websites.
| Item | Calories | Protein (g) | Fat (g) | Carbohydrates (g) | Sodium (mg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taco Bell Bean and Cheese Burrito | 380 | 12 | 12 | 60 | 830 |
| Subway 6-inch Veggie Delite (with black beans) | 280 (estimated, based on similar Subway options) | 10 | 6 | 50 | 660 (estimated) |
| Chipotle Softshell Burrito (Black Beans and Rice) | 500-700 (variable depending on fillings) | 15-25 (variable) | 15-25 (variable) | 70-100 (variable) | 800-1200 (variable) |
Dietary Considerations and Implications

The Taco Bell Bean and Cheese Burrito, while a convenient and affordable meal, presents several considerations for individuals with specific dietary needs and those aiming for optimal health. Understanding its nutritional profile is crucial for making informed choices about its inclusion in a balanced diet. Regular consumption requires careful evaluation of its impact on various health aspects.The burrito’s suitability varies greatly depending on individual dietary requirements.
Its vegetarian status is a significant advantage for those avoiding meat, but its vegan status is questionable depending on the specific ingredients and potential cross-contamination during preparation. Sodium content is notably high, posing a challenge for individuals on low-sodium diets. Furthermore, its relatively high carbohydrate and calorie count needs to be factored into weight management strategies.
Suitability for Various Diets
The Taco Bell Bean and Cheese Burrito is naturally vegetarian, as it contains no meat products. However, it is not definitively vegan due to the potential for cross-contamination with dairy or other non-vegan ingredients during preparation or handling. Individuals following a strict vegan diet should inquire directly with Taco Bell about their preparation methods and potential cross-contamination risks. The high sodium content makes it unsuitable for those on low-sodium diets, who should either avoid it or opt for a smaller portion.
Understanding Taco Bell bean and cheese burrito nutrition requires considering its ingredients. A key component is the cheese, and comparing its nutritional profile to other cheeses can be insightful. For instance, you might compare it to the nutritional content of Babybel cheese, readily available information on which can be found here: babybel cheese nutrition information. This comparison helps illustrate the varying nutritional values in different cheese types and contributes to a more informed understanding of the Taco Bell burrito’s overall nutritional impact.
For individuals managing their carbohydrate intake, the burrito’s carbohydrate content should be considered within their daily limits.
Impact of Regular Consumption on Overall Health, Taco bell bean and cheese burrito nutrition
Regular consumption of the Taco Bell Bean and Cheese Burrito could contribute to weight gain if not balanced with other healthy food choices and regular physical activity. Its high calorie and carbohydrate content, combined with a relatively low fiber content, can lead to fluctuations in blood sugar levels. The high sodium content poses a risk for individuals prone to hypertension.
While the burrito provides some protein and certain vitamins and minerals, it lacks the diversity and balance of nutrients found in a well-rounded diet. For example, a person consuming this burrito daily as a primary source of nutrition may experience deficiencies in essential vitamins and minerals found in fruits and vegetables. To mitigate these risks, individuals should incorporate a variety of nutrient-rich foods into their diet to compensate for the burrito’s nutritional limitations.
Dietary Considerations and Potential Implications
The following points summarize the dietary considerations and potential implications of regularly consuming Taco Bell Bean and Cheese Burritos:
- High Sodium Content: Contributes to high blood pressure in susceptible individuals.
- High Carbohydrate Content: Can lead to blood sugar spikes and weight gain if not balanced with other foods and physical activity.
- Moderate Protein Source: Provides some protein, but not a complete source of all essential amino acids.
- Low Fiber Content: May contribute to digestive issues if not combined with high-fiber foods.
- Limited Micronutrient Content: Lacks a wide range of vitamins and minerals found in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Potential for Cross-Contamination (Vegan Concerns): May not be suitable for strict vegans due to potential cross-contamination with non-vegan ingredients.
- Weight Management Implications: Regular consumption without mindful portion control and physical activity can contribute to weight gain.
Serving Size and Calorie Information
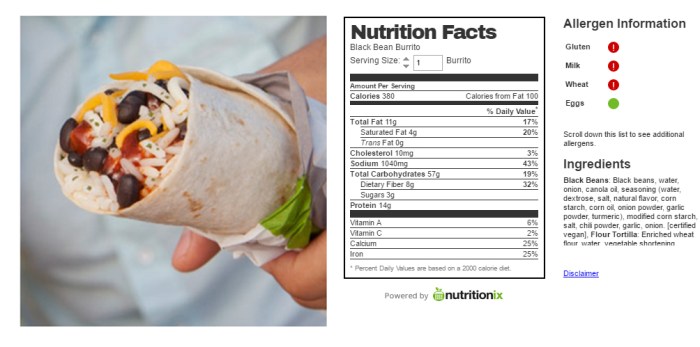
Understanding the serving size and calorie content of a Taco Bell Bean and Cheese Burrito is crucial for managing daily caloric intake and making informed dietary choices. This information allows consumers to accurately track their nutrition and plan meals effectively. Accurate data ensures that individuals can align their food choices with their health goals.The official serving size for a Taco Bell Bean and Cheese Burrito, as stated on their nutritional information, is one burrito.
While the exact calorie count may vary slightly depending on preparation and location, the generally advertised calorie count per serving is approximately 380 calories. Calculating the calories per 100g requires converting the weight of the burrito, which isn’t consistently provided by Taco Bell, but can be estimated based on similar products. A reasonable estimate places the calorie count per 100g around 150-180 calories.
However, it is important to consult the most up-to-date nutritional information available directly from Taco Bell’s website or in-store materials for the most accurate figures.
Serving Size Impact on Nutritional Value and Calorie Intake
Serving size significantly influences the overall nutritional value and calorie intake derived from a food item. Consuming more than one Bean and Cheese Burrito will naturally increase both the calorie count and the quantity of nutrients consumed, proportionally. For instance, eating two burritos would double the calorie intake to approximately 760 calories, and similarly increase the amounts of protein, carbohydrates, and fat.
Conversely, consuming only half a burrito would reduce the calorie and nutrient intake by half. This highlights the importance of paying close attention to serving sizes when considering the nutritional impact of any food, including the Taco Bell Bean and Cheese Burrito. Accurate portion control is key to achieving dietary goals. Using measuring tools or visual guides can aid in accurate portioning.
Essential Questionnaire
Is the Taco Bell Bean and Cheese Burrito gluten-free?
Taco Bell does not explicitly market this burrito as gluten-free. Cross-contamination during preparation is a possibility, so individuals with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity should exercise caution.
What is the sodium content of the burrito?
The sodium content varies depending on the specific preparation and serving size. Refer to the official Taco Bell nutritional information for the most accurate data.
Does the burrito contain any artificial sweeteners or preservatives?
Checking the ingredient list on Taco Bell’s website or the packaging is necessary to determine the presence of artificial sweeteners or preservatives. This information can fluctuate.
How does the burrito compare to a homemade bean and cheese burrito in terms of nutrition?
A homemade version typically offers greater control over ingredients and allows for healthier substitutions, potentially leading to a lower sodium and fat content, and higher fiber content. Nutritional comparisons require specific ingredient lists for both.


